Compact Stepper Motor Controller for Cerna Components

- Operate Motorized Microscopy Stages and Components
- 7.0 A Peak Current Output
- Three Channel Control via Software or Three-Knob Joystick
MCMK3
3-Knob Joystick
MCM301 Used to Control
the PMP2XY Cerna®
Translating Platform
MCM301
Compact Controller for Motorized Rigid Stands and PLS Series Stages

Please Wait
| Compatible Stages |
|---|
| MPM250(/M) Motorized Rigid Stand PLSX & PLSXY Translation Stages for Rigid Stands PLSZ Motorized Focusing Module PMP2XY(/M) XY Translation Platform MMP2XY Microscope Body Translator |

Click to Enlarge
MCM301 Controller and MCMK3 Three-Knob Joystick Used to Control Both Axes of the PLSXY Translation Stage and One-Axis MPM250 Motorized Rigid Stand
Features
- Operate Motorized Microscopy Stages and Components
- Control up to Three Channels at Once through Standalone Software
- Each Axis can be Individually Disabled to Prevent Unintended Movements or to Retain a Position
- MCMK3 Three-Knob Joystick Allows Hand Operation (Sold Separately)
- Dial on top of Joystick Adjusts Translation Speed
The MCM301 Stepper Motor Controller is designed to remotely control the motorized microscopy stages and components listed in the table above using standalone software. The MCMK3 Three-Knob Joystick (sold separately) can be connected to the controller to provide hand operation. The MCM301 controller supports plug-and-play operation, automatically detecting compatible stages that are connected to it. An interlock circuit is included, with the interlock jack located on the front panel of the controller.
Since each MCM301 controller has three channels, you only need to purchase enough channels for each of the modules you intend to drive. For example, an MPM250 Vertical Rigid Stand (which has one axis) and a PLSXY Translation Stage (two axes) would only require one MCM301 controller.
Translation can be adjusted remotely via the software (see the Software tab for details). Alternatively, a LabVIEW™, C++, and Python software development kit (SDK) and support documentation are available to integrate the controller with custom imaging software.
Each controller ships with a power supply and region-specific power cord. If a replacement is needed, the DS24 Power Supply can be used.
Joystick Operation
The MCMK3 three-knob joystick includes a rotation knob and push-button switch dedicated to a single axis on each side face. The push-button switch enables and disables the axis and is lit in green when the axis is enabled. Disabling the axis lets the user preserve a position or prevent accidental movements. A dial on the top face of the joystick adjusts the velocity per rotation of the knob. For more information on the MCMK3 three-knob joystick and how to utilize the USB HID protocol, please see the full web presentation. Note that the MCMK3 three-knob joystick is the only joystick compatible with the MCM301 controller.
| Item # | MCM301 |
|---|---|
| Motor Output |
|
| Motor Drive Voltage |
24 V |
| Motor Drive Current | 7.0 A (Peak), 3.0 A (RMS) |
| Motor Drive Type | 12-Bit PWM Control |
| Control Algorithm | Open/Closed-Loop Microstepping |
| Stepping | 128 Microsteps per Full Step |
| Encoder Resolution | - |
| Total Steps per Revolution | - |
| Maximum Stepping Velocity | - |
| Position Feedback | 5 V Quadrature Encoder (QEP) Input |
| Encoder Feedback Bandwidth | 1 MHz |
| Position Counter | 32 Bit |
| Operating Modes | Position and Velocity |
| Velocity Profile |
Trapezoid |
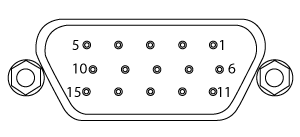
| Motor Drive Connector |
|
| Mechanical Specifications | 15 Position D-Type, Female Pin Connector |
| Motor Drive Outputs | Phase A and B |
| Quadrature Encoder (QEP) Input |
Single Ended |
| Limit Switch Inputs | Forward, Reverse (+ Common Return) |
| Encoder Supply | 5 V |
| Input Power Requirements | |
| Voltage | 24 VDC |
| Current | 6.67 A |
| General | |
| Computer Connection |
USB 2.0 |
| Housing Dimensions (W x D x H) |
5.91" x 4.52" x 1.91" (150.0 mm x 114.8 mm x 48.5 mm) |
| Compatible Motor Specifications | ||
|---|---|---|
| Motor Type | 2-Phase Bi-Polar Stepper | |
| Rated Phase Current | Up to 7 A Peak | |
| Coil Resistance (Nominal) | 5 to 20 Ω | |
| Position Control | Open or Closed Loop | |
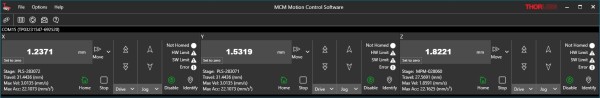
MCM301 Software
Links to the latest versions of the MCM301 controller software and firmware are below. The software download page includes a GUI, drivers, and a LabView™/C++/Python software development kit (SDK) for third-party development support.
Click to Enlarge
MCM301 Controller Software

Click to Enlarge
MCM301 Contents
Each MCM301 controller includes the following:
- Controller Box
- Power Supply, with Location-Specific Power Cord
- USB Cable (A to B)
Note: The MCM301 does not include a knob box. A compatible MCMK3 three-knob joystick is available separately.
| Posted Comments: | |
seonghwan kim
(posted 2023-12-05 09:10:48.057) Good morning, I am using the MCM3000 and MCM3001 with a PLS-XY stage. I want to control them using LabVIEW. Therefore, I utilized your SDK (MCM3000, v.40) and example. However, I am encountering an issue at the initial step. When I attempt to use the 'Find device.vi,' it fails to detect the device. I am utilizing it with COM32, and when I use your MCM3000.exe, it operates correctly. Best, Kim. cdolbashian
(posted 2023-12-13 03:36:49.0) Thank you for reaching out to us with this inquiry! I think perhaps the example code you are using might not be the most up-to-date one. I have reached out to you directly with the correct example. Peter Doyle
(posted 2023-09-05 09:29:00.307) Goop Morning,
It would be very helpful to be able to buy replacement cables. I am particularly interested in replacement joystick cables.
Best Regards,
Peter Doyle cdolbashian
(posted 2023-09-11 01:38:40.0) Thank you for reaching out to us with this inquiry! We can certainly sell you the cables you need directly, even if they aren't on the web catalogue. I have contacted you directly to facilitate this. For future similar inquiries, please contact techsupport@thorlabs.com. Qu Zhelin
(posted 2022-09-22 16:48:31.08) We misplaced the power adapter of MCM3001, now we need to buy it again, but we don't know its model, we can only judge its company by the "MW" on the picture, could you please tell us the model of the power adapter? ksosnowski
(posted 2022-09-26 11:12:32.0) Hello Qu, thanks for reaching out to Thorlabs. We can quote replacement power supply accessory for the MCM3001 as a special item. These requests can be directed to techsupport@thorlabs.com or your region's local tech support team. I have reached out directly to discuss this further. Chia-Hsien Lin
(posted 2020-02-10 21:41:00.333) Hi,
I try to use Labview to control the MCM3002 control with the version 4.0 driver. Is it possible to control the motor speed in the Labview? On the other hand, even if I call the parameter "PARAM_X_VELOCITY_CURRENT" by the commend "GetParam()", the value will return zero.
Best,
Chia-Hsien llamb
(posted 2020-02-21 08:12:59.0) Thank you for your feedback. The software cannot adjust the speed of the connected stage. Only the Speed Control knob can adjust the speed of translation per rotation of each knob when using the 3-Axis Knob Box to manually control a connected stage, as speed control is hard-wired to this dial. I have reached out to you directly to discuss further. Dmytro Toptunov
(posted 2019-08-05 08:26:43.31) Good morning,
Does MCM3003 work with LNR50SE/M stages? They are also built around DRV014 stepper motor, but not mentioned in the MCM3003 supported equipment list.
Does MCM3003 support mixed configuration, e.g. 2 x LNR50S/M stages and 1 x LNR50SE/M stage?
Finally, could you please send an LabVIEW SDK and manuals?
Best regards,
Dmytro nbayconich
(posted 2019-08-16 08:43:31.0) Thank you for conctacting Thorlabs. The MCM3003 controller can be used with the encoded LNR50SE stages, the only downside is that the encoder can not be used with the MCM3003 controller. You can use a combination of either the LNR50S or LNR50SE just be aware that the encoder cannot be used with this particular controller, in order to have access to the encoders feedback you would have to use a controller like the BSC203 with the LNR50SE stages.
Our SDK can be downloaded directly from our webpage under the software download link below.
https://www.thorlabs.us/software_pages/ViewSoftwarePage.cfm?Code=MCM3000
I will reach out to you directly. Matthew Broome
(posted 2019-07-03 05:35:19.95) Does the SDK for this controller support integration with MatLab? asundararaj
(posted 2019-07-08 02:59:06.0) Thank you for contacting Thorlabs. At the moment, we do not have dedicated documentation/support for integration with MATLAB. However, we do have documentation for serial communication which can be used to integrate with MATLAB. I have reached out to you directly for further discussion. Seonho Shin
(posted 2019-05-27 00:30:41.94) 'MCM3001 and ZFS2020' seems to work only on Windows 7. It does not work well when run on Windows 10. When I ordered just '0.1mm' move, It keeps going until the upper limit.
It there other version of application or SDK which is compatible for Windows 10? YLohia
(posted 2019-06-13 08:51:25.0) Hello, thank you for contacting Thorlabs. We believe this to be a configuration issue rather than a software or hardware issue (and should not be dependent on the OS being used). Does the problem show up for any motion or just 0.1mm? What version of the software are you using? We reached out to you directly at the time of your original post to troubleshoot your issue. If you still have this problem, please send us an email with the screenshots of your GUI. chris
(posted 2017-07-21 16:19:51.013) +1 for adding the SDK/software/examples + manual to the website. Since it isn't there right now, could you send it to me directly? tfrisch
(posted 2017-07-26 11:43:08.0) Hello, thank you for contacting Thorlabs. It looks like our previous attempt to send you this file was returned because it contained a zip attachment. I will reach out to you directly about posting this in a place you can download it directly. craig
(posted 2017-01-11 12:30:26.1) The product MCM3001 has no manual available online. It would also be helpful if the SDK and LAbview examples were available for direct download rather than by contacting tech support. Your main office does not have any information to support this product and I was directed to contact the imaging group. tfrisch
(posted 2017-01-11 01:24:23.0) Hello, thank you for contacting Thorlabs. I will reach out to you directly about your application. |
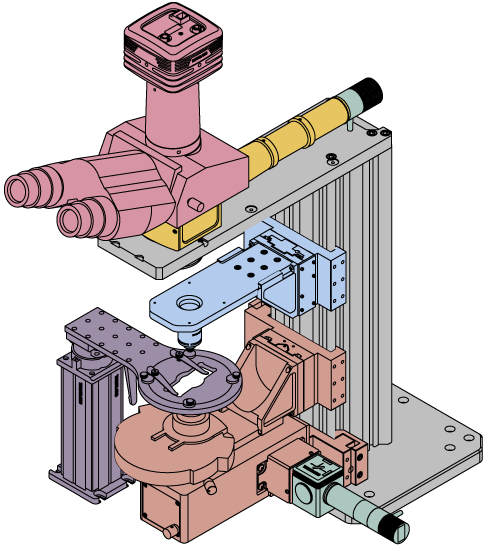
Click on the different parts of the microscope to explore their functions.
Elements of a Microscope
This overview was developed to provide a general understanding of a Cerna® microscope. Click on the different portions of the microscope graphic to the right or use the links below to learn how a Cerna microscope visualizes a sample.
Terminology
Arm: Holds components in the optical path of the microscope.
Bayonet Mount: A form of mechanical attachment with tabs on the male end that fit into L-shaped slots on the female end.
Bellows: A tube with accordion-shaped rubber sides for a flexible, light-tight extension between the microscope body and the objective.
Breadboard: A flat structure with regularly spaced tapped holes for DIY construction.
Dovetail: A form of mechanical attachment for many microscopy components. A linear dovetail allows flexible positioning along one dimension before being locked down, while a circular dovetail secures the component in one position. See the Microscope Dovetails tab or here for details.
Epi-Illumination: Illumination on the same side of the sample as the viewing apparatus. Epi-fluorescence, reflected light, and confocal microscopy are some examples of imaging modalities that utilize epi-illumination.
Filter Cube: A cube that holds filters and other optical elements at the correct orientations for microscopy. For example, filter cubes are essential for fluorescence microscopy and reflected light microscopy.
Köhler Illumination: A method of illumination that utilizes various optical elements to defocus and flatten the intensity of light across the field of view in the sample plane. A condenser and light collimator are necessary for this technique.
Nosepiece: A type of arm used to hold the microscope objective in the optical path of the microscope.
Optical Path: The path light follows through the microscope.
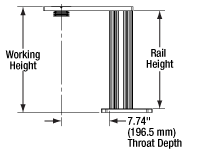
Rail Height: The height of the support rail of the microscope body.
Throat Depth: The distance from the vertical portion of the optical path to the edge of the support rail of the microscope body. The size of the throat depth, along with the working height, determine the working space available for microscopy.
Trans-Illumination: Illumination on the opposite side of the sample as the viewing apparatus. Brightfield, differential interference contrast (DIC), Dodt gradient contrast, and darkfield microscopy are some examples of imaging modalities that utilize trans-illumination.
Working Height: The height of the support rail of the microscope body plus the height of the base. The size of the working height, along with the throat depth, determine the working space available for microscopy.
 Click to Enlarge
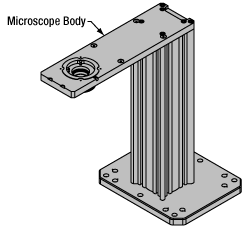
Click to EnlargeCerna Microscope Body
Click to Enlarge
Body Details
Microscope Body
The microscope body provides the foundation of any Cerna microscope. The support rail utilizes 95 mm rails machined to a high angular tolerance to ensure an aligned optical path and perpendicularity with the optical table. The support rail height chosen (350 - 600 mm) determines the vertical range available for experiments and microscopy components. The 7.74" throat depth, or distance from the optical path to the support rail, provides a large working space for experiments. Components attach to the body by way of either a linear dovetail on the support rail, or a circular dovetail on the epi-illumination arm (on certain models). Please see the Microscope Dovetails tab or here for further details.
 Click to Enlarge
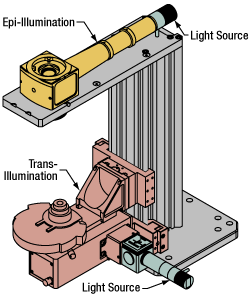
Click to EnlargeIllumination with a Cerna microscope can come from above (yellow) or below (orange). Illumination sources (green) attach to either.
Illumination
Using the Cerna microscope body, a sample can be illuminated in two directions: from above (epi-illumination, see yellow components to the right) or from below (trans-illumination, see orange components to the right).
Epi-illumination illuminates on the same side of the sample as the viewing apparatus; therefore, the light from the illumination source (green) and the light from the sample plane share a portion of the optical path. It is used in fluorescence, confocal, and reflected light microscopy. Epi-illumination modules, which direct and condition light along the optical path, are attached to the epi-illumination arm of the microscope body via a circular D1N dovetail (see the Microscope Dovetails tab or here for details). Multiple epi-illumination modules are available, as well as breadboard tops, which have regularly spaced tapped holes for custom designs.
Trans-illumination illuminates from the opposite side of the sample as the viewing apparatus. Example imaging modalities include brightfield, differential interference contrast (DIC), Dodt gradient contrast, oblique, and darkfield microscopy. Trans-illumination modules, which condition light (on certain models) and direct it along the optical path, are attached to the support rail of the microscope body via a linear dovetail (see Microscope Dovetails tab or here). Please note that certain imaging modalities will require additional optics to alter the properties of the beam; these optics may be easily incorporated in the optical path via lens tubes and cage systems. In addition, Thorlabs offers condensers, which reshape input collimated light to help create optimal Köhler illumination. These attach to a mounting arm, which holds the condenser at the throat depth, or the distance from the optical path to the support rail. The arm attaches to a focusing module, used for aligning the condenser with respect to the sample and trans-illumination module.
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Epi-Illumination Modules | Breadboards & Body Attachments |
Brightfield | DIC | Dodt | Condensers | Condenser Mounting | Light Sources |
 Click to Enlarge
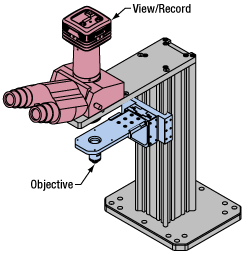
Click to EnlargeLight from the sample plane is collected through an objective (blue) and viewed using trinocs or other optical ports (pink).
Sample Viewing/Recording
Once illuminated, examining a sample with a microscope requires both focusing on the sample plane (see blue components to the right) and visualizing the resulting image (see pink components).
A microscope objective collects and magnifies light from the sample plane for imaging. On the Cerna microscope, the objective is threaded onto a nosepiece, which holds the objective at the throat depth, or the distance from the optical path to the support rail of the microscope body. This nosepiece is secured to a motorized focusing module, used for focusing the objective as well as for moving it out of the way for sample handling. To ensure a light-tight path from the objective, the microscope body comes with a bellows (not pictured).
Various modules are available for sample viewing and data collection. Trinoculars have three points of vision to view the sample directly as well as with a camera. Double camera ports redirect or split the optical path among two viewing channels. Camera tubes increase or decrease the image magnification. For data collection, Thorlabs offers both cameras and photomultiplier tubes (PMTs), the latter being necessary to detect fluorescence signals for confocal microscopy. Breadboard tops provide functionality for custom-designed data collection setups. Modules are attached to the microscope body via a circular dovetail (see the Microscope Dovetails tab or here for details).
 Click to Enlarge
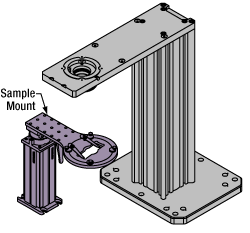
Click to EnlargeThe rigid stand (purple) pictured is one of various sample mounting options available.
Sample/Experiment Mounting
Various sample and equipment mounting options are available to take advantage of the large working space of this microscope system. Large samples and ancillary equipment can be mounted via mounting platforms, which fit around the microscope body and utilize a breadboard design with regularly spaced tapped through holes. Small samples can be mounted on rigid stands (for example, see the purple component to the right), which have holders for different methods of sample preparation and data collection, such as slides, well plates, and petri dishes. For more traditional sample mounting, slides can also be mounted directly onto the microscope body via a manual XY stage. The rigid stands can translate by way of motorized stages (sold separately), while the mounting platforms contain built-in mechanics for motorized or manual translation. Rigid stands can also be mounted on top of the mounting platforms for independent and synchronized movement of multiple instruments, if you are interested in performing experiments simultaneously during microscopy.
 Products Home
Products Home




































 Compact Controllers for Microscopy
Compact Controllers for Microscopy