Minimize Sample Substitution Errors When Using Integrating Spheres


Please Wait
Sample Substitution Errors

Click to Enlarge
Figure 1.1 Measuring diffuse sample transmittance and reflectance as shown here can result in a distorted sample spectrum due to sample substitution error. The problem is that the reflectivity over the sample area is different during the reference and sample measurements.
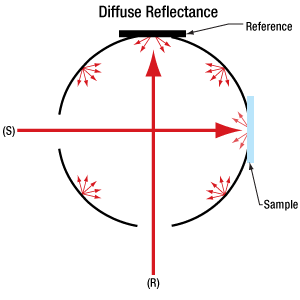
Click to Enlarge
Figure 1.2 This configuration is not susceptible to sample substitution error, since the interior of the sphere is the same for reference and sample measurements. During the reference measurement the light travels along (R), and no light is incident along (S). The opposite is true when a sample measurement is made.
Absolute transmittance and absolute diffuse reflectance spectra of optical samples can be found using integrating spheres. These spectra are found by performing spectral measurements of both the sample of interest and a reference.
Measurement of a reference is needed since this provides the spectrum of the illuminating light source. Obtaining the reference scan allows the spectrum of the light source to be subtracted from the sample measurement.
The light source reference measurement is made with no sample in place for transmittance data and with a highly reflective white standard reference sample in place for reflectance measurements.
Sample substitution errors incurred while acquiring the sample and reference measurement sets can negatively effect the accuracy of the corrected sample spectrum, unless the chosen experimental technique is immune to these errors.
Conditions Leading to Sample Substitution Errors
An integrating sphere's optical performance depends on the reflectance at each point on its entire inner surface. Often, a section of the sphere's inner wall is replaced by the sample when its transmittance and diffuse reflectance spectra are measured (Figure 1.1). However, modifying a section of the inner wall alters the performance of the integrating sphere.
Sample substitution errors are a concern when the measurement procedure involves physically changing one sample installed within the sphere for another. For example, when measuring diffuse reflectance (Figure 1.1, bottom), a first measurement might be made with the standard reference sample mounted inside the sphere. Next, this sample would be removed and replaced by the sample of interest, and a second measurement would be acquired. Both data sets would then be used to calculate the corrected absolute diffuse reflectance spectrum of the sample.
This procedure would result in a distorted absolute sample spectrum. Since the sample of interest and the standard reference have different absorption and scattering properties, exchanging them alters the reflectivity of the integrating sphere over the samples' surface areas. Due to the average reflectivity of the integrating sphere being different for the two measurements, they are not perfectly compatible.
Solution Option: Install Sample and Reference Together
One experimental technique that avoids sample substitution errors acquires measurement data when both sample and reference are installed inside the integrating sphere at the same time (Figure 1.2). This approach requires an integrating sphere large enough to accomodate the two, as additional ports.
The light source is located external to the integrating sphere, and measurements of the sample and standard reference are acquired sequentially. The specular reflection from the sample, or the transmitted beam, is often routed out of the sphere, so that only the diffuse light is detected. Since the inner surface of the sphere is identical for both measurements, sample substitution errors are not a concern.
Alternate Solution Option: Make Measurements from Sample and Reference Ports
If it is not possible to install both sample and standard references in the integrating sphere at the same time, it is necessary to exchange the installed sample. If this must be done, sample substitution errors can be removed by following the procedure detailed in [1].
This procedure requires a total of four measurements. When the standard sample is installed, measurements are made from two different ports. One has a field of view that includes the sample and the other does not. The sample of interest is then subsituted in and the measurements are repeated. Performing the calculations described in [1] using these measurements removes the sample substitution errors.
References
[1] Luka Vidovic and Boris Majaron, "Elimination of single-beam substitution error in diffuse reflectance measurements using an integrating sphere," J. Biomed.Opt. 19, 027006 (2014).
|
Looking for more Insights? |
Date of Last Edit: Dec. 4, 2019 |
| Posted Comments: | |
| No Comments Posted |
 Products Home
Products Home Integrating Sphere Sample Substitution Error
Integrating Sphere Sample Substitution Error