Pellin Broca Prism

- Ideal for Wavelength Separation of a Beam of Light
- Selected Wavelength Deviated by 90°
ADBU-20
ADB-10
Application Idea
ADB-10 Mounted on a
PRMTZ8 Motorized Rotation Stage

Please Wait
Common Specifications
- Dimensional Tolerances: ±0.2 mm
- Angular Tolerances: ±3 min
- Surface Flatness: λ/8
- Surface Quality: 20-10 Scratch Dig
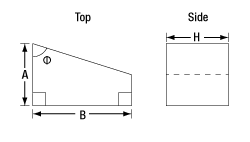
| Item # | A | B | H | Φ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADB-10 | 19.0 mm | 33.0 mm | 11.0 mm | 78° 26' |
| ADB-20 | 38.0 mm | 66.0 mm | 22.0 mm | 78° 26' |
| ADBU-10 | 19.0 mm | 33.0 mm | 11.0 mm | 78° 26' |
| ADBU-20 | 38.0 mm | 66.0 mm | 22.0 mm | 78° 26' |
| ADBV-10 | 19.0 mm | 33.0 mm | 11.0 mm | 78° 26' |
Features
- Ideal for Wavelength Seperation of a Beam of Light
- Selected Wavelength Deviated by 90°
Pellin Broca Prisms can be used to separate the harmonics of a laser beam or compensate for group velocity dispersion. The light enters and exits the prism near Brewster's angle, which minimizes reflection losses in P-polarized light. Since the beam undergoes one total internal reflection before exiting the prism, the angle between the input and exit beams is 90° plus a small angle due to dispersion. The dispersion is less for longer wavelengths.
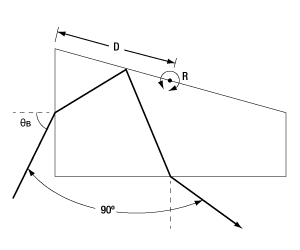
As the prism is rotated about point R in the figure to the right, the wavelength of light that is deviated by 90° changes even though the geometry and relative positions of the input and output beams remains unchanged.
| Click on the red Document icon next to the item numbers below to access the Zemax file download. Our entire Zemax Catalog is also available. |
| Item # | Material | Design Spectrum λlow to λhighb |
Angular Separation Between λlow & λhigh |
Brewster's Angle θB for λlow to λhigh |
Distance D (Rotation Point) |
Aperture (Square) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADB-10 | N-BK7a | 380 nm - 2.5 μm | 5.42° | 56.1° - 56.9° | 16.1 mm | 10 mm |
| ADB-20 | N-BK7a | 380 nm - 2.5 μm | 5.42° | 56.1° - 56.9° | 32.2 mm | 20 mm |
| ADBU-10 | UV Fused Silicaa | 190 - 425 nm | 11.47° | 55.7° - 57.4° | 16.1 mm | 10 mm |
| ADBU-20 | UV Fused Silicaa | 190 - 425 nm | 11.47° | 55.7° - 57.4° | 32.2 mm | 20 mm |
| ADBV-10 | Calcium Fluoridea | 180 - 250 nm | 5.23° | 55.7° - 56.6° | 16.1 mm | 10 mm |
Selection Guide for Prisms
Thorlabs offers a wide variety of prisms, which can be used to reflect, invert, rotate, disperse, steer, and collimate light. For prisms and substrates not listed below, please contact Tech Support.
Beam Steering Prisms
| Prism | Material | Deviation | Invert | Reverse or Rotate | Illustration | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Right Angle Prisms | N-BK7, UV Fused Silica, Calcium Fluoride, or Zinc Selenide | 90° | 90° | No |  |
90° reflector used in optical systems such as telescopes and periscopes. |
| 180° | 180° | No |  |
180° reflector, independent of entrance beam angle. Acts as a non-reversing mirror and can be used in binocular configurations. |
||
| TIR Retroreflectors (Unmounted and Mounted) and Specular Retroreflectors (Unmounted and Mounted) |
N-BK7 | 180° | 180° | No |  |
180° reflector, independent of entrance beam angle. Beam alignment and beam delivery. Substitute for mirror in applications where orientation is difficult to control. |
| Unmounted Penta Prisms and Mounted Penta Prisms |
N-BK7 | 90° | No | No | 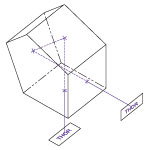 |
90° reflector, without inversion or reversal of the beam profile. Can be used for alignment and optical tooling. |
| Roof Prisms | N-BK7 | 90° | 90° | 180o Rotation | 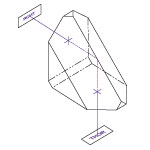 |
90° reflector, inverted and rotated (deflected left to right and top to bottom). Can be used for alignment and optical tooling. |
| Unmounted Dove Prisms and Mounted Dove Prisms |
N-BK7 | No | 180° | 2x Prism Rotation | 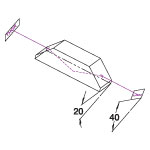 |
Dove prisms may invert, reverse, or rotate an image based on which face the light is incident on. Prism in a beam rotator orientation. |
| 180° | 180° | No | 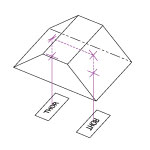 |
Prism acts as a non-reversing mirror. Same properties as a retroreflector or right angle (180° orientation) prism in an optical setup. |
||
| Wedge Prisms | N-BK7 | Models Available from 2° to 10° | No | No | 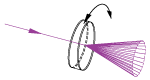 |
Beam steering applications. By rotating one wedged prism, light can be steered to trace the circle defined by 2 times the specified deviation angle. |
| No | No | 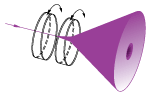 |
Variable beam steering applications. When both wedges are rotated, the beam can be moved anywhere within the circle defined by 4 times the specified deviation angle. |
|||
| Coupling Prisms | Rutile (TiO2) or GGG | Variablea | No | No | 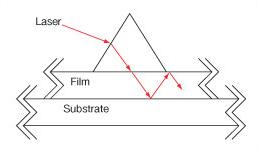 |
High index of refraction substrate used to couple light into films. Rutile used for nfilm > 1.8 GGG used for nfilm < 1.8 |
Dispersive Prisms
| Prism | Material | Deviation | Invert | Reverse or Rotate | Illustration | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Equilateral Prisms | F2, N-F2, N-SF11, Calcium Fluoride, or Zinc Selenide |
Variablea | No | No | 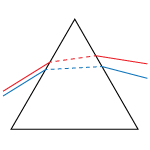 |
Dispersion prisms are a substitute for diffraction gratings. Use to separate white light into visible spectrum. |
| Dispersion Compensating Prism Pairs | Fused Silica, Calcium Fluoride, SF10, or N-SF14 | Variable Vertical Offset | No | No | 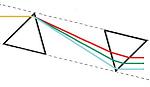 |
Compensate for pulse broadening effects in ultrafast laser systems. Can be used as an optical filter, for wavelength tuning, or dispersion compensation.
|
| Pellin Broca Prisms | N-BK7, UV Fused Silica, or Calcium Fluoride |
90° | 90° | No | 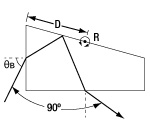 |
Ideal for wavelength separation of a beam of light, output at 90°. Used to separate harmonics of a laser or compensate for group velocity dispersion. |
Beam Manipulating Prisms
| Prism | Material | Deviation | Invert | Reverse or Rotate | Illustration | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anamorphic Prism Pairs | N-KZFS8 or N-SF11 |
Variable Vertical Offset | No | No |  |
Variable magnification along one axis. Collimating elliptical beams (e.g., laser diodes) Converts an elliptical beam into a circular beam by magnifying or contracting the input beam in one axis. |
| Axicons (UVFS, ZnSe) | UV Fused Silica or Zinc Selenide |
Variablea | No | No |
Creates a conical, non-diverging beam with a Bessel intensity profile from a collimated source. |
Polarization Altering Prisms
| Prism | Material | Deviation | Invert | Reverse or Rotate | Illustration | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glan-Taylor, Glan-Laser, and α-BBO Glan-Laser Polarizers | Glan-Taylor: Calcite Glan-Laser: α-BBO or Calcite |
p-pol. - 0° s-pol. - 112°a |
No | No | 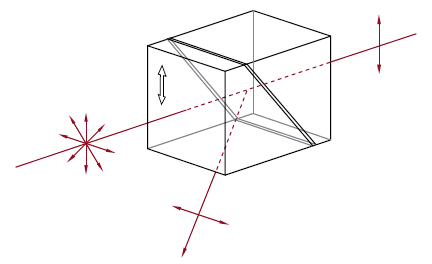 |
Double prism configuration and birefringent calcite produce extremely pure linearly polarized light. Total Internal Reflection of s-pol. at the gap between the prism while p-pol. is transmitted. |
| Rutile Polarizers | Rutile (TiO2) | s-pol. - 0° p-pol. absorbed by housing |
No | No | 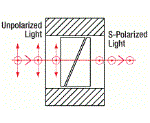 |
Double prism configuration and birefringent rutile (TiO2) produce extremely pure linearly polarized light. Total Internal Reflection of p-pol. at the gap between the prisms while s-pol. is transmitted.
|
| Double Glan-Taylor Polarizers | Calcite | p-pol. - 0° s-pol. absorbed by housing |
No | No | 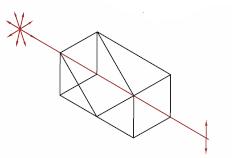 |
Triple prism configuration and birefringent calcite produce maximum polarized field over a large half angle. Total Internal Reflection of s-pol. at the gap between the prism while p-pol. is transmitted. |
| Glan Thompson Polarizers | Calcite | p-pol. - 0° s-pol. absorbed by housing |
No | No |  |
Double prism configuration and birefringent calcite produce a polarizer with the widest field of view while maintaining a high extinction ratio. Total Internal Reflection of s-pol. at the gap between the prism while p-pol. is transmitted. |
| Wollaston Prisms and Wollaston Polarizers |
Quartz, Magnesium Fluoride, α-BBO, Calcite, Yttrium Orthovanadate | Symmetric p-pol. and s-pol. deviation angle |
No | No | 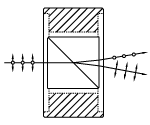 |
Double prism configuration and birefringent calcite produce the widest deviation angle of beam displacing polarizers. s-pol. and p-pol. deviate symmetrically from the prism. Wollaston prisms are used in spectrometers and polarization analyzers. |
| Rochon Prisms | Magnesium Fluoride or Yttrium Orthovanadate |
Ordinary Ray: 0° Extraordinary Ray: deviation angle |
No | No |  |
Double prism configuration and birefringent MgF2 or YVO4 produce a small deviation angle with a high extinction ratio. Extraordinary ray deviates from the input beam's optical axis, while ordinary ray does not deviate. |
| Beam Displacing Prisms | Calcite | 2.7 or 4.0 mm Beam Displacement | No | No |  |
Single prism configuration and birefringent calcite separate an input beam into two orthogonally polarized output beams. s-pol. and p-pol. are displaced by 2.7 or 4.0 mm. Beam displacing prisms can be used as polarizing beamsplitters where 90o separation is not possible. |
| Fresnel Rhomb Retarders | N-BK7 | Linear to circular polarization Vertical Offset |
No | No | 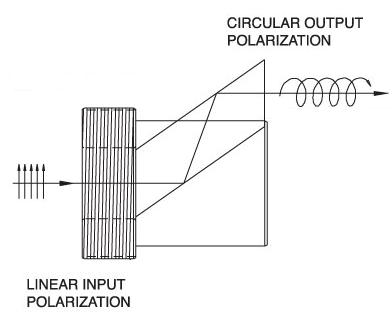 |
λ/4 Fresnel Rhomb Retarder turns a linear input into circularly polarized output. Uniform λ/4 retardance over a wider wavelength range compared to birefringent wave plates. |
| Rotates linearly polarized light 90° | No | No |  |
λ/2 Fresnel Rhomb Retarder rotates linearly polarized light 90°. Uniform λ/2 retardance over a wider wavelength range compared to birefringent wave plates. |
Beamsplitter Prisms
| Prism | Material | Deviation | Invert | Reverse or Rotate | Illustration | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beamsplitter Cubes | N-BK7 | 50:50 splitting ratio, 0° and 90° s- and p- pol. within 10% of each other |
No | No |  |
Double prism configuration and dielectric coating provide 50:50 beamsplitting nearly independent of polarization. Non-polarizing beamsplitter over the specified wavelength range. |
| Polarizing Beamsplitter Cubes | N-BK7, UV Fused Silica, or N-SF1 | p-pol. - 0° s-pol. - 90° |
No | No |  |
Double prism configuration and dielectric coating transmit p-pol. light and reflect s-pol. light. For highest polarization use the transmitted beam. |
| Posted Comments: | |
user
(posted 2023-10-13 16:34:06.207) Do you have a technical drawing showing where the rotation point is in regards to the other facets? Also the lengths of all the sides? cdolbashian
(posted 2023-10-27 11:25:20.0) Thank you for reaching out to us with this inquiry! All of the requested information is shown within the "Overview" tab on the product page. I have reached out to you directly to share the explicit values with you. jon.freeman
(posted 2016-01-13 11:01:15.14) What is the angular tolerance of the "fine ground" sides to the polished faces -we want to use the prism as an angular reference besembeson
(posted 2016-01-18 10:31:55.0) Response from Bweh at Thorlabs USA: I will contact you with this information please. tcohen
(posted 2012-03-09 13:30:00.0) Response from Tim at Thorlabs: We are able to offer custom coatings on some of our optics. I have contacted you directly to get more information. michael.renner
(posted 2012-03-07 10:12:12.0) Do you also offer a coated version of ADB-10 when working with s-polarized light (antireflection between 420 - 580nm)? |
 Products Home
Products Home








 Pellin Broca Prisms
Pellin Broca Prisms