Fresnel Rhomb Retarders

- Broad Wavelength Range: 400 - 1550 nm
- λ/2 and λ/4 Retardance
- SM1-Threaded Mount
FR600QM
FR600HM
FR600QM in an
LMR1 Fixed
Optic Mount

Please Wait
Click to Enlarge
Click Here for Raw Data File
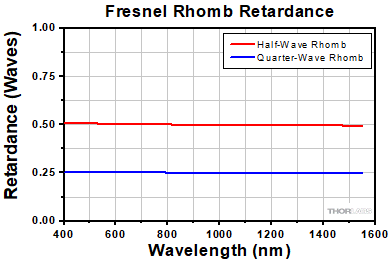
The retardance data above illustrates the relatively wavelength-independent design of these rhombs for the specified wavelength range.
Features
- Quarter-Wave or Half-Wave Retardance
- Broader Wavelength Range than Waveplates
- Cemented Prisms (FR600HM)
Fresnel Rhomb Retarders act like broadband waveplates providing uniform λ/4 or λ/2 retardance over a wider range of wavelengths than possible with birefringent waveplates. They can replace retardation plates for broadband, multi-line, or tunable laser sources.
The rhomb is designed so that a 45° phase shift occurs at each internal reflection creating a total retardance of λ/4. Because the phase shift is a function of the slowly varying rhomb dispersion, the retardance change with wavelength is much lower than other types of retarders. The half-wave retarder combines two quarter-wave rhombs. These mounted versions are engraved with the part number and are SM1-threaded, allowing for easy installation using Thorlabs rotation mounts like the RSP1 and PRM1.
| Specifications | ||
|---|---|---|
| Item # | FR600QM | FR600HM |
| Retardance | λ/4 | λ/2 |
| Retardance Variation | 2% for 600 - 1550 nm (Typical) 5% @ 400 nm (Max) |
|
| Material | N-BK7a | |
| Wavelength Range | 400 - 1550 nm | |
| Clear Aperture | Ø10.0 mm +0.0 / -0.1 mm | |
| Surface Quality of Input and Output Faces |
20-10 Scratch-Dig | |

Click to Enlarge
SM1-Threaded (1.035"-40) Mount Engraved with Item Description and Fast Axis Orientation
| Click on the red Document icon next to the item numbers below to access the Zemax file download. Our entire Zemax Catalog is also available. |
 Click to Enlarge
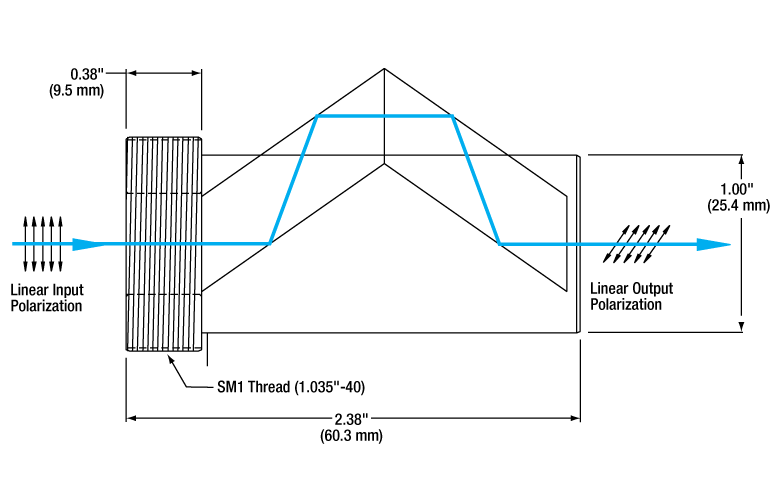
Click to EnlargeBeam path shown in blue. To achieve an output polarization that is rotated with respect to the initial polarization, the input polarization must not be aligned with the fast or slow axis.
 Click to Enlarge
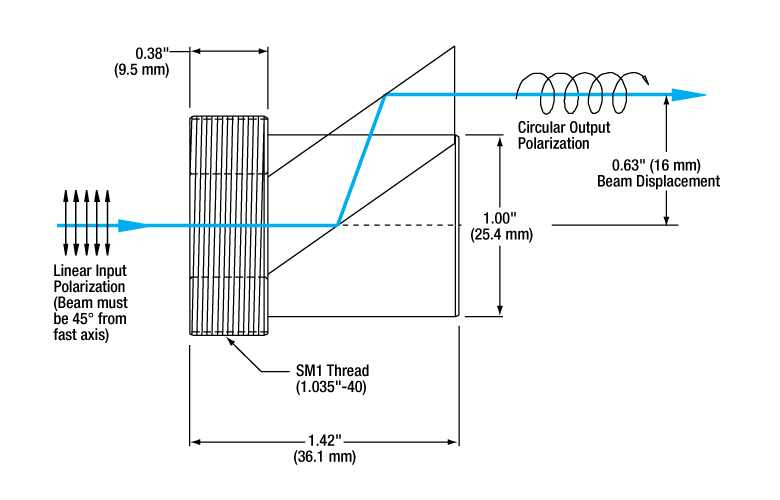
Click to Enlarge Beam path shown in blue. To achieve circular output polarization, the beam must have an initial polarization that is 45° from the fast axis, engraved on the retarder.
| Posted Comments: | |
Kenny Huang
(posted 2022-05-03 15:29:10.217) Hi Thorlabs,
Could you provide the transmission rate throughout the usable range of wavelengths?
And I'd like to confirm that it'll work to act as a transformer to bring the incident P-pol. beam to S-pol. after passing through this 1/4 retarder back and forth.
I tried to use it with PBS instead of non polarized BS to received more reflected broadband energy. cdolbashian
(posted 2022-05-04 04:44:30.0) Thank you for reaching out to us with this inquiry Kenny. As your application seems to require bidrectional operation yielding polarization rotation in the same angular direction, you would likely have success using a Faraday rotator rather than a simple phase plate. I have reached out to you to discuss your application, potential alternatives, and the transmission data which you have requested. Roberto Myers
(posted 2021-08-02 16:28:56.13) the data for wavelength dependence only goes to 400nm. It would be useful to know the data from 200-400nm as well. YLohia
(posted 2021-08-05 01:22:16.0) Thank you for contacting Thorlabs. Extended range data can be requested by emailing techsupport@thorlabs.com. I have reached out to you directly with this data. Oriol Arteaga
(posted 2020-03-01 15:39:31.663) Can you sell just the threaded mount where these rhombs are mounted? llamb
(posted 2020-03-03 04:16:42.0) Yes, we can indeed sell the threaded mount component as a custom/nonstandard item. For future reference, you may reach out to techsupport@thorlabs.com directly for custom quote requests. We have reached out to you directly in this particular case to set up a quote. Hsin-Yu Wu
(posted 2019-09-17 19:30:15.9) Do you have a Fresnel rhomb that is designed in such a way that a 22.5° phase shift occurs at each internal reflection? By the internal reflections at four surfaces (just like FR600HM), this Fresnel rhomb creates a total retardance of λ/4 and has co-axial input and output without the beam displacement of 16 mm. YLohia
(posted 2019-09-18 10:04:08.0) Hello, thank you for contacting Thorlabs. Custom optics can be requested by emailing techsupport@thorlabs.com. We have reached out to you directly to discuss this further. Please also see our Achromatic Quarter Wave Plates (https://www.thorlabs.com/newgrouppage9.cfm?objectgroup_id=854) and Superachromatic Quarter Wave Plates (https://www.thorlabs.com/newgrouppage9.cfm?objectgroup_id=2193), as these produce a retardance of λ/4 without beam displacement. user
(posted 2019-08-08 18:06:40.83) Do you have any adaptor for FR600QM to be used in a 30mm cage system? We are having a difficulty to use the FR600QM in our cage system, because of the offset in the beam path. Thanks YLohia
(posted 2019-08-09 09:37:13.0) Hello, thank you for contacting Thorlabs. Components from this page (https://www.thorlabs.com/newgrouppage9.cfm?objectgroup_id=4125) can be used to accommodate for the 16mm beam deviation from the fresnel rhomb. For example, you could either use C3A or C5A to set the next cage plate at a different height with respect to the one containing the FR600QM. Another option would be using a few cascading ER90B pieces to add height to a cage assembly. sukhyun kim
(posted 2019-06-19 13:52:34.71) I love this product FR600QM but I wish I have a bit smaller version. As I rotate this with the ingoing beam position fixed, the outgoing beam draws a circle with the radius 16mm. Can I have a bit smaller version to draws a circle with the radius 10mm, which is attached to the same size 1 inch diameter circular frame (SM1) as the original version? YLohia
(posted 2019-07-09 09:44:25.0) Hello, thank you for contacting Thorlabs. Is there any reason the AQWP05M-600 does not work for your application? It will introduce minimal beam walk with rotation. I have reached out to you directly to discuss the possibility of a custom option. vincent.jarlaud
(posted 2019-02-14 17:59:11.733) Can the Fresnel rhombs be used with a longer wavelength than 1550 nm as long as it remains in the transmission range of N-BK7 ? YLohia
(posted 2019-02-18 08:58:22.0) Hello, thank you for contacting Thorlabs. Yes, these Fresnel rhombs can indeed be used at longer wavelengths, however, the transmission will rapidly drop below 50% for wavelengths >2000nm. I will reach out to you directly with some data. pidgai
(posted 2017-03-16 10:57:34.69) Hello, ThorLabs. Our laboratory bought FR600HM. We mounted it in KS1RS to rotate our polarization. But we observe that both refracted and passed beams Precess wile rotating angle wheel on KS1RS. How to solve this problem? tfrisch
(posted 2017-03-23 10:10:26.0) Hello, thank you for contacting Thorlabs. I will reach out to you directly to troubleshoot this. It would be good to know the size of the precessed circle and whether beam traces a cone or cylinder. jakob.kilgus
(posted 2017-02-23 08:30:24.887) Is it possible for you to manufacture the fresnel rhomb from ZnSe, in order to work in the midIR? tfrisch
(posted 2017-03-03 09:01:41.0) Hello, thank you for contacting Thorlabs. I have posted your need for an MIR Fresnel Rhomb in our internal engineering forum, and I will reach out to you directly. clement.fallet
(posted 2015-10-14 15:08:53.393) What is the angular acceptance of a Fresnel rhomb? Can it be used with slightly focused light, e.G. NA = 0.05? besembeson
(posted 2015-10-16 11:54:24.0) Response from Bweh at Thorlabs USA: This works based on the principle of phase change from total internal reflection at two points (quarter-wave) and four points (half-wave) so your input beam should be collimated and at normal incidence. peter.vanderwalle
(posted 2014-12-10 10:58:56.34) I have the same question as deden below. Looking forward to the updated specs. myanakas
(posted 2015-04-02 04:47:02.0) Response from Mike at Thorlabs: Thank you for your feedback and we apologize for the delay in our response. We have looked into our manufacturing process and cannot guarantee the angle deviation or vertical/horizontal offsets of our Fresnel rhomb retarders at this time. However, we are always reassessing our manufacturing process and will keep this feedback in mind and add it to the website when possible. In the meantime, if deviations and its offsets that can result from the assembly process are an issue, then we recommend using a standard waveplate. agokmen52
(posted 2014-04-15 09:49:54.887) I want to modify a UV-VIS spectrometer for Circular Dichroism measurement. I needed quarter wave retarder for right and left circularly polarized light. Your Fresnel Rhomb Retarders wavelength range is 400-1550 nm. Do you have retarders covering UV range as well? Would you please advise me for retarders and polarizers needed for a CD spectrometer? pbui
(posted 2014-04-22 05:06:25.0) The proper waveplates and polarizers you will need will depend on your operating wavelengths. We will contact you to discuss your application in greater detail and to provide extended performance data for the FR600QM. andrew_yablon
(posted 2013-12-04 16:03:29.443) What is the cost for a FR600HM with a "C" anti-reflection coating (1000nm to 1600nm) on the entrance and exit faces?
Thank you tcohen
(posted 2013-12-05 03:00:28.0) Response from Tim at Thorlabs: Thanks for your inquiry! We can provide customs such as this through our technical team at techsupport@thorlabs.com. An applications engineer will contact you with a quote. deden
(posted 2013-10-18 06:23:48.587) What is the pointing stability of your half wave Fresnel rhomb? What are the angular and offset deviations? tcohen
(posted 2013-10-31 04:20:17.0) Response from Tim at Thorlabs: Thank you for contacting us. We are testing typical values and will post an update shortly. user
(posted 2013-10-07 03:50:09.747) Can the Fresnel Rhomb retarders work bi-directionally? cdaly
(posted 2013-10-10 15:53:00.0) Response from Chris at Thorlabs: Yes, these would work equally well in either orientation. apalmentieri
(posted 2010-02-15 13:52:22.0) A response from Adam at Thorlabs to bdougherty: You are correct, the Fresnel Rhomb retarders do not have AR coatings on the input or output faces. A custom coating can be supplied if needed. I will contact you via email to see if you are interested in this option. bdougherty
(posted 2010-02-15 13:02:42.0) May I presume that the input and output faces
have no AR coating? Thanks. osulliva
(posted 2009-07-31 12:18:43.0) Your drawing of the Fresnel Rhomb on the Drawings tab is misleading. The output polarization is only circular when the input polarization is polarized at 45 degrees (50% s- and 50% p-polarized at the surface where the total internal reflection occurs). As shown, it looks like the polarization is just p-polarized, in which case the Fresnel Rhomb does not alter the polarization state. |
 Products Home
Products Home








 Fresnel Rhombs
Fresnel Rhombs